Study Guide 1
Quizzes will be closed book. You can bring one written cheat sheet. 30 minutes in class.
Topics:
-
UNIX commands
-
Programming in C
-
Data types and sizes
-
Function stacks
-
Basic arrays
Write C programs to check your answers. Or you can ask a TA or instructor to give feedback on your responses.
Practice questions
1) What is the minimum size of the following structures and variables? If the variable is a pointer, give the size of the memory that the pointer points to.
A)
struct Snack {
char name[32];
int quantity;
float cost;
};
B)
struct Snack snacks[2];
C)
struct Snack* snacks = malloc(sizeof(struct Snack) * 10);
D)
char message[16];
E)
int values[2];Hint: To check your answers, use the sizeof() function.
2) Consider navigating directories from the command prompt in UNIX. Suppose you are in your home directory.
-
How would you create a subdirectory with name
foo? -
How would you see the contents of your
.bashrcfile? -
How would you list the contents of
foo? -
How can you create a file in the directory
foocalledtest.c? -
How can you compile a c program?
3) Suppose Willa is in their home directory, /home/willa. Write commands to produce the following directory structure.
Willa contains two sub-directories, A ad B, and one file hello.c. B contains a sub-directory C and file test.txt.
Below is a visualization of it where child directories are indented.
\home\willa
A
B
C
test.txt
hello.c4) When Willow runs her program from the command line, she gets the following error? What is happening and how can she fix it?
$ ls
Makefile fortune fortune.c hello hello.c
$ hello
Command 'hello' not found5) The following program crashes. What is the problem and how can we fix it?
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int* value = NULL;
int a = 4;
printf("value is %d\n", *value);
}6) The following program crashes. What is the problem and how can we fix it?
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
void initialize(char text[]) {
strcpy(text, "pina collada");
}
int main() {
char str1[5];
initialize(str1);
printf("%s\n", str1);
return 0;
}7) What is the output of this program?
#include <stdio.h>
int arg_modifier(int x, int *y);
int main() {
int val1, val2, ret;
printf("Enter a value: ");
scanf("%d", &val1);
printf("Enter another value: ");
scanf("%d", &val2);
// pass val1 by value and val2 by pointer:
printf("before call: val1 = %d val2 = %d\n", val1, val2);
ret = arg_modifier(val1, &val2);
printf("after call: val1 = %d val2 = %d ret = %d\n", val1, val2, ret);
return 0;
}
int arg_modifier(int x, int *y) {
printf(" in arg_modifier: x = %d *y = %d\n", x, *y);
*y = *y + x;
x = x + 5;
printf(" leaving arg_modifier: x = %d *y = %d\n", x, *y);
// Draw function stack here
return x;
}8) Draw the state of the function stack and heap for the program above in arg_modifier. Assume the
user entered the values 6 and 1. Draw the stack at the point in the execution
right before the return from the arg_modifier function, and consider the
following questions:
-
Where are variables val1 and val2 located on the stack?
-
Where are the parameter values located?
-
What value does each parameter get?
-
What variables are in scope of
arg_modifier?
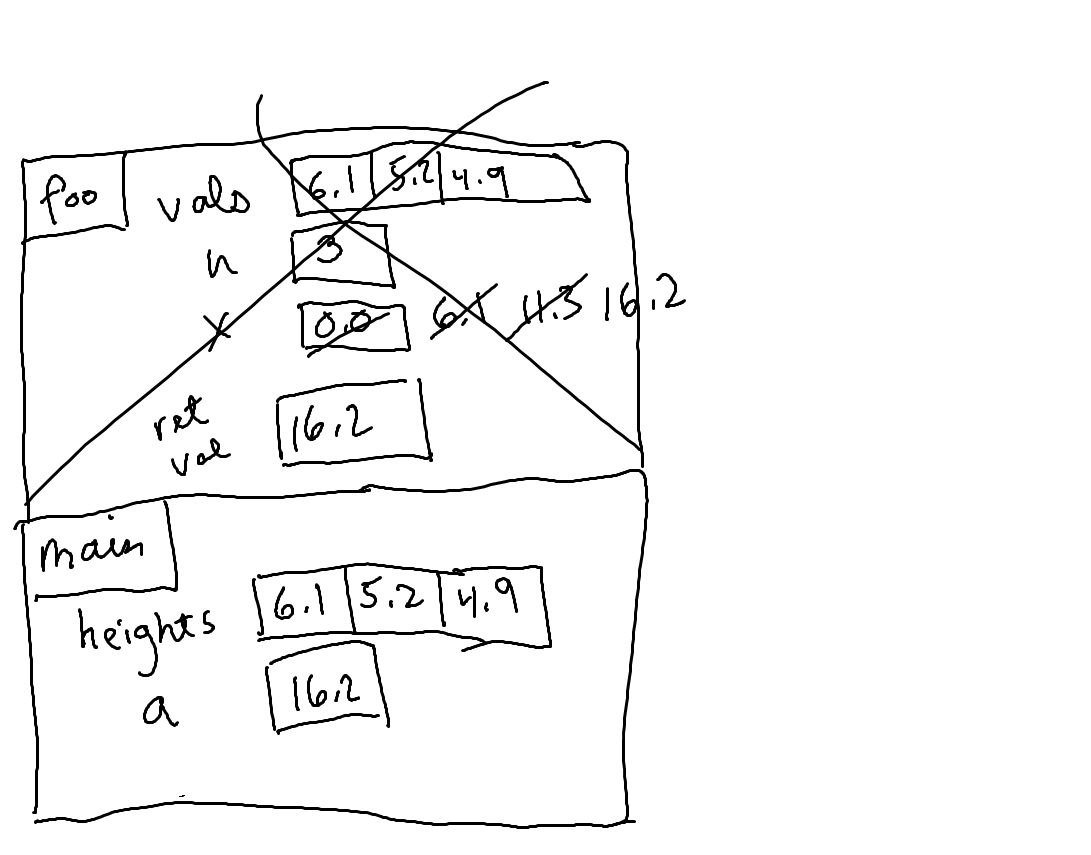
9) Consider the following code. Find and fix the errors in the associated stack diagram.
float foo(float* vals, int n)
{
float x = 0.0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
x += vals[i];
}
return x;
}
void main()
{
float heights[3] = {6.1f, 5.2f, 4.9f};
float a = foo(heights, 3);
float b = a / 3;
// draw stack here
printf("%.2f\n", b);
}
10) Write code that implements a power function (for positive integer exponents only). A call to your function should compute \(base^{exp}\) and might look like:
result = power(base, exp);11) Write code that implements a function void removeLetter(char* str, char letter) that removes all occurrences of letter
from str. Your function should modify the contents of str. (To check your work, implement your program and test it from main).
12) Write code that implements a function isPalindrome that returns 1 if a given string is a palindrome and 0 otherwise.
Your function can be iterative or recursive. Test your function from main.
13) Draw the directory hierarchy that corresponds to the following commands
$ pwd
/home/alinen
$ mkdir A
$ cd A
$ mkdir Z
$ touch talk.c
$ cd ..
$ touch listen.c
$ cd
$ touch sing.c14) Consider the following directory structure
root
> home
>> ren
>>> A
>> stimpy
>>> B
>>> C
>>>> hello.txt-
Draw the directory hierarchy above as a tree.
-
What is the absolute path of hello.txt?
-
If we are in the directory A, what is the relative path of hello.txt?
-
If we are in the directory B, what is the relative path of hello.txt?